Desalination can be a vital engineering for supplying contemporary water in several areas of the entire world, however it comes along with its possess set of advantages and disadvantages. This is a breakdown:
Advantages of Desalination:
one. Trustworthy H2o Supply: It offers a steady and reliable supply of fresh drinking water, unbiased of rainfall or neighborhood h2o sources.
two. Drought Resilience: Desalination is a must have in drought-susceptible locations, guaranteeing a continuous drinking water source even for the duration of severe droughts.
3. Drinking water Security: It improves drinking water stability for regions dependent on drinking water imports or These with minimal freshwater resources.
4. Supports Agriculture and Sector: By furnishing new drinking water, desalination supports agriculture and field in arid regions, contributing to economic balance and expansion.
five. Ecosystem Conservation: By supplementing natural water sources, it decreases the need to extract drinking water from delicate ecosystems, helping to protect biodiversity.
6. Technological Innovation: Desalination drives progress in water therapy technological innovation, which often can profit other parts of h2o administration and conservation.
seven. Scalability and suppleness: Desalination vegetation can be scaled to accommodate the needs of little communities or huge cities, and they can be located near coastal areas where the necessity for contemporary drinking water is usually greatest.
Drawbacks of Desalination:
one. Significant Electricity Usage: Classic desalination processes, especially reverse osmosis and thermal distillation, are energy-intense, resulting in higher operational expenses and opportunity environmental impacts.
two. Environmental Effect: The discharge of highly concentrated brine again to the ocean can harm marine ecosystems. Also, the ingestion course of action could be harmful to maritime existence.
three. Value: The initial set up and ongoing operational expenses of desalination vegetation are substantial, earning the water manufactured more expensive than that from standard resources.
four. Carbon Footprint: Unless of course run by renewable Power resources, desalination crops contribute to greenhouse gasoline emissions because of their higher Electricity consumption.
5. Infrastructure and Servicing: Desalination crops need complex infrastructure and typical servicing, that may be difficult in remote or fewer created regions.
six. Limited to Coastal Places: Most desalination vegetation are feasible only in the vicinity of sea coasts, restricting their applicability for landlocked regions Unless of course high-priced transportation is associated.
seven. Potential for Pollution: Devoid of right administration, the procedure can deliver unsafe chemical byproducts, contributing to air pollution.
Balancing the Scales:
The decision to use desalination normally arrives down to a stability in between the urgent want for fresh h2o and also the likely environmental and financial charges. In several locations, the main advantages of having a trustworthy drinking water offer outweigh the cons, especially as know-how developments and will become a lot more effective and environmentally friendly. For others, the higher prices and environmental fears enable it to be a fewer feasible option. As a result, It really is normally part of a broader approach that includes water conservation, recycling, along with the use of other drinking water resources.
Desalination, while generally mentioned concerning its issues and environmental impacts, also provides numerous environmental Added benefits, significantly in regions experiencing critical drinking water scarcity. Here is how desalination is often advantageous to the setting:
one. Delivers a Reliable H2o Supply:
- Desalination delivers a gradual, local climate-impartial source of drinking water. This is particularly vital in arid locations where by traditional resources are insufficient or non-existent, cutting down the strain on overused rivers, lakes, and underground aquifers.
2. Supports Ecosystems and Agriculture:
- By furnishing an alternate source of new h2o, desalination may help preserve all-natural freshwater ecosystems Which may in any other case be depleted for human use. Furthermore, it supports agriculture in arid areas, marketing food protection and reducing the need to divert drinking water from delicate ecosystems.
3. Cuts down More than-Extraction of Freshwater:
- In many aspects of the entire world, the demand from customers for freshwater leads to the about-extraction of rivers and groundwater, resulting in environmental harm like habitat loss and land subsidence. Desalination can lower this pressure by supplementing the freshwater supply.
4. Prospective for Renewable Electrical power Integration:
- Contemporary desalination plants are significantly working with renewable Vitality sources, for example solar or wind electrical power. This not merely lowers the carbon footprint of desalination and also promotes The expansion of renewable Electricity infrastructure, contributing to your broader environmental reward.
5. Encourages Drinking water Recycling and Innovation:
- The process of desalination encourages technological innovation in h2o management. Several crops are made to recycle and reuse water throughout the plant, resulting in much more effective water use In general. Developments in desalination technology generally spill above into other parts of h2o administration, endorsing conservation and productive use in many sectors.
6. Increases Human Wellbeing and Improvement:
- Although not a direct environmental gain, furnishing reliable access to thoroughly clean water increases general public health and socioeconomic advancement. Much healthier populations with secure livelihoods are much better equipped to manage and treatment for his or her pure methods, leading to better environmental stewardship.
seven. Drought Resilience:
- Desalination gives regions prone to droughts using a consistent h2o source, mitigating the impacts of drought on human populations along with the natural environment. This aids reduce the overuse of scarce all-natural water for the duration of drought durations, preserving ecosystems and wildlife.
eight. Possible for Brine Utilization:
- Investigate is ongoing into approaches to use the byproduct Desalination Plant Manufacturer brine, for instance in salt extraction, aquaculture, or at the same time as a raw product for certain industries. Making use of brine might help mitigate its environmental affect and switch a squander product or service right into a useful resource.
Conclusion:
Whilst desalination does pose environmental challenges, significantly linked to Strength use and brine disposal, its Rewards in offering a steady, trusted supply of new h2o can lead positively to environmental sustainability, particularly when combined with renewable Vitality and impressive technologies. As technological innovation advances as well as the effectiveness of desalination increases, its role in environmental management and h2o sustainability continues to mature.
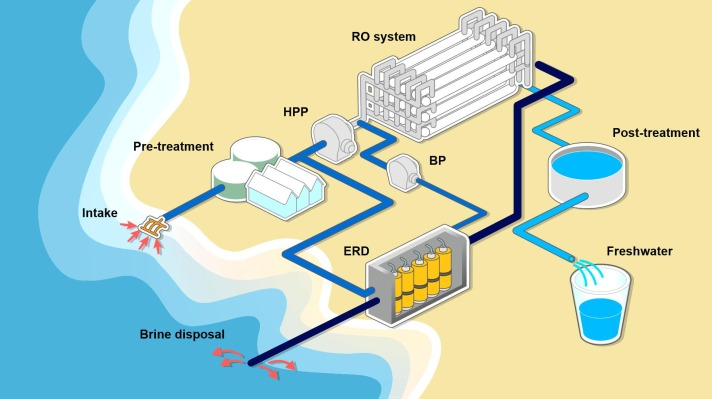
Desalination is the entire process of taking away salt together with other minerals from saline h2o to create fresh new drinking water that is well suited for human usage, irrigation, and other takes advantage of. This is the way it typically operates:
1. Consumption:
Saltwater, usually in the ocean or briny groundwater, is taken to the desalination plant.
2. Pre-remedy:
The ingestion drinking water is pre-dealt with to eliminate particles and sediments. This action could possibly include filtration along with the addition of chemical compounds to forestall the growth of organisms that may foul the technique.
three. Desalination (Key Course of action):
There are 2 Principal approaches utilised:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO):
- The pre-handled h2o is pressured by means of semi-permeable membranes beneath large stress.
- The membranes allow for drinking water molecules to go through but block salt as well as other impurities.
- This method needs significant Strength, primarily to develop the stress necessary to thrust h2o with the membranes.
- Thermal Distillation:
- Procedures like Multi-Stage Flash (MSF) or Multi-Influence Distillation (MED) involve heating the saltwater.
- The h2o evaporates, leaving the salts behind, then the vapor is condensed to sort fresh new drinking water.
- These strategies are frequently Employed in locations the place energy, specifically from waste warmth or fossil fuels, is relatively inexpensive.
4. Publish-procedure:
- The desalinated drinking water may very well be remineralized or have its pH altered to really make it ideal for its supposed use.
- Minerals could be included again to create the water flavor improved and to fulfill wellbeing requirements for consuming h2o.
5. Brine Disposal:
- The leftover brine (very concentrated saltwater) and other squander products need to be diligently disposed of, generally by returning it to The ocean. Appropriate disposal is critical to minimize environmental effects, since the significant salt concentration can hurt marine ecosystems.
Electricity and Environmental Factors:
- Desalination is energy-intensive, significantly reverse osmosis. Endeavours to create the procedure extra efficient and environmentally sustainable include things like employing renewable Vitality resources and improving membrane engineering to call for less stress and Vitality.
- Environmental issues also involve the effect of brine disposal on marine daily life and also the carbon footprint with the Electrical power resources employed.
Desalination is really an significantly important technology, specifically in locations the place fresh drinking water is scarce. Developments in technologies and energy effectiveness are making it a far more viable option for providing contemporary drinking water to populations throughout the world.